Now we have to introduce the concepts of the ways in which something like light or sound can travel. Sound cannot travel in space because it is a wave travelling in air, water or a solid object which conducts (carrys) the waves. Think of a still pond of water into which you drop a stone. The ripples are like the sound, and your ear will hear them when they reach the edge (your ear).
Light is different. It travels well in space where thre is nothing to block its way, and it travels through air because air has enough space between the solid parts of the atom (mainly Nitrogen and Oxygen in normal air), to let it pass. Light travels through glass, but is reflected off a polished silver surface (a mirror), and to a lesser extent most other polished or flat surfaces where the molecules are all of a very similar size.
What happens to light when it is absorbed by a solid object? Well we don't know for certain what happens to it, but mostly we think it is turned into heat, and increases teh energy levl of that object slightly, but not by very much because light has very little mass. It takes a lot of light to give much energy.
Solar energy has other components which help it to transmit energy. These are energies of the electromagnetic spectrum, including magnetism, and electromagnetic radiation of various wavelengths, including visible light of several different colours (wavelengths), gamma radiation, microwaves, radio waves, infra red radiation (heat), and ultraviolet radiation, to name but a few.
Electromagnetic radiation (often abbreviated E-M radiation or EMR) is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. EMR has both electric and magnetic field components, which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation.
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that form the basis for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between the forces acting on a body and its motion due to those forces. They have been expressed in several different ways over nearly three centuries,[2] and can be summarized as follows:
- First law: The velocity of a body remains constant unless the body is acted upon by an external force.[3][4][5]
- Second law: The acceleration a of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inversely proportional to the mass m, i.e., F = ma.
- Third law: The mutual forces of action and reaction between two bodies are equal, opposite and collinear.
The three laws of motion were first compiled by Sir Isaac Newton in his work Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published on July 5, 1687.[6] Newton used them to explain and investigate the motion of many physical objects and systems.[7] For example, in the third volume of the text, Newton showed that these laws of motion, combined with his law of universal gravitation, explained Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
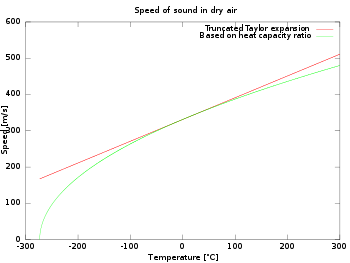
Approximation of the speed of sound in dry air based on the heat capacity ratio (in green) against the truncated Taylor expansion (in red).
In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point.
The concept of a Taylor series was formally introduced by the English mathematician Brook Taylor in 1715. If the Taylor series is centered at zero, then that series is also called a Maclaurin series, named after the Scottish mathematician Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the 18th century.
It is common practice to approximate a function by using a finite number of terms of its Taylor series. Taylor's theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error in this approximation. Any finite number of initial terms of the Taylor series of a function is called a Taylor polynomial. The Taylor series of a function is the limit of that function's Taylor polynomials, provided that the limit exists. A function may not be equal to its Taylor series, even if its Taylor series converges at every point. A function that is equal to its Taylor series in an open interval (or a disc in the complex plane) is known as an analytic function.
